Spread
Kudzu can expand vegetatively through runners and rhizomes. The vine roots at nodes to create new plants. Kudzu can also be spread occasionally by seed. Spread by seed may be increased where the giant resin bee (Megachile sculpturalis), a pollinator, occurs. This species of bee is native to Asia but has been introduced into the U.S.
Lookalikes
Kudzu can be confused with several native species, including poison ivy, hog peanut, wild grape, and bur cucumber. Wild grape and bur cucumber have simple leaves. There are several native plants in the legume family that resemble kudzu, but their leaves are usually not as large and these plants usually do not have the aggressive growth habit that kudzu has. Kudzu vines often smother trees and ground vegetation, creating a monoculture.
Control
Kudzu is very difficult to control. Some manual options include aggressive mowing and cutting below the node crowns. For chemical control, products with the active ingredient triclopyr are very effective as foliar or basal bark applications. If using chemical control, follow label directions and apply in a manner consistent with federal and state laws.
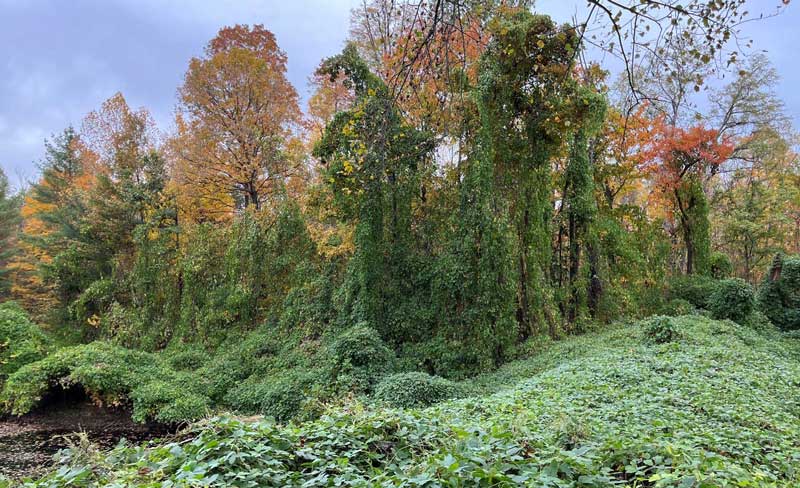


 Alternate, compound, three broad leaflets up to 4 inches across. Leaflets may be entire or lobed with hairy margins.
Alternate, compound, three broad leaflets up to 4 inches across. Leaflets may be entire or lobed with hairy margins.