GIARDIASIS
Cases
= 736White = 6.7
Nonwhite = 2.4
Gender-specific rates
(per 100,000 population)Female = 11.5
Male = 10.9
Transmission
Giardiasis is a flagellate protozoan infection transmitted most commonly by ingestion of cysts in fecally contaminated water and from person-to-person by hand-to-mouth transfer of cysts from the feces of infected individuals.
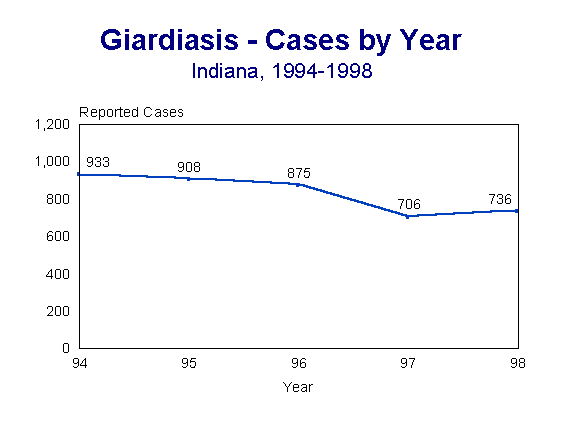
There were 736 cases of giardiasis reported in 1998 which represented a slight increased over the previous year (Figure 1). This was still lower than the previous 5 year average incidence (883 cases/year).
Figure 1.

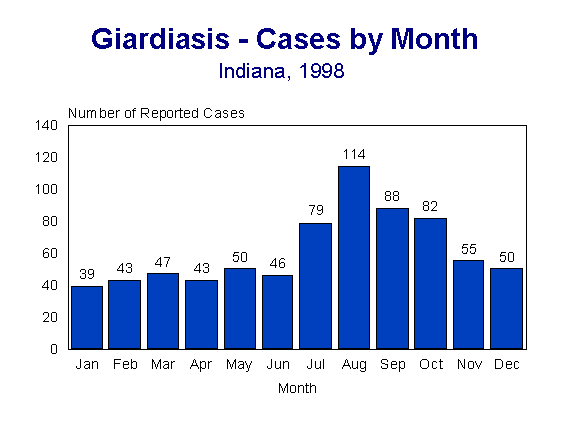
The number of reported cases was highest during the late summer and early autumn months (Figure 2). The increase during warm weather months may indicate increased exposure to contaminated surface water during outdoor activities.
Figure 2.
While the rate of giardiasis infection by gender was similar, the age-adjusted rate of giardiasis was 2.8 times higher for whites than nonwhites.
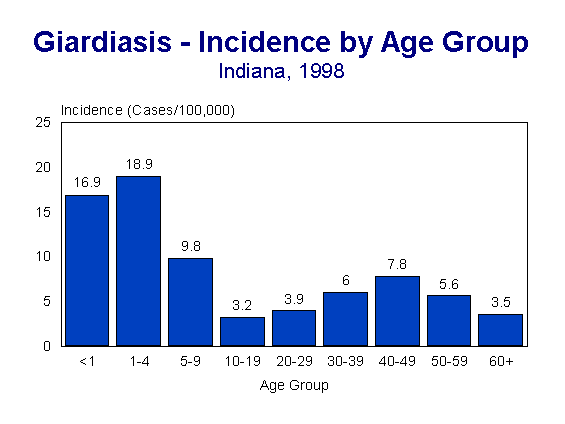
(Figure 3) shows that the age-specific rates were highest among children aged one to four years (18.9), followed by children under age one (16.9). Nationally, outbreaks of giardiasis have been occurring with more frequency in day care centers.
Figure 3.
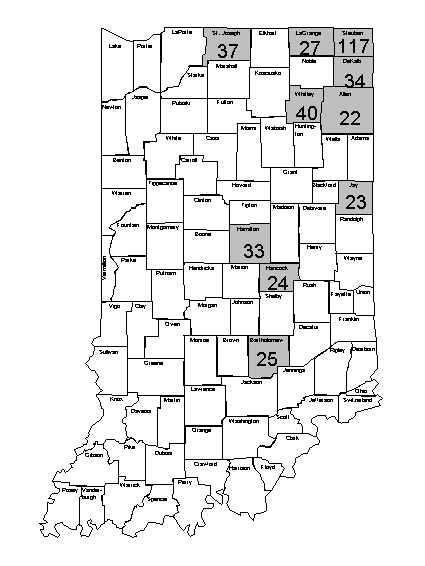
Among counties with at least 5 cases reported, the incidence rates were highest in Steuben (116.6), Whitley (39.8), St. Joseph (37.2), DeKalb (34.0), Hamilton (33.1), Lagrange (27.1), Bartholomew (25.1), Hancock (24.2), Jay (23.2), and Allen (22.3) counties (Figure 4)..
Figure 4. Giardiasis Incidence Rate by County
(among counties with > 5 reported cases)
Indiana, 1998
[an error occurred while processing this directive]