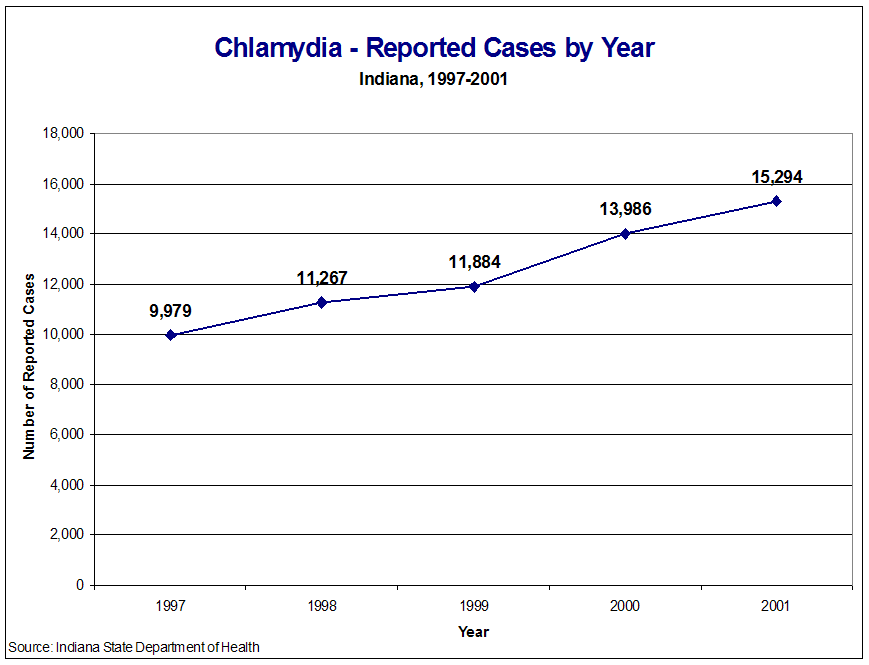
Figure Chl1: Chlamydia - Reported Cases by Year, Indiana, 1997-2001
2001 Indiana Report of Infectious Diseases |
View ISDH's basic facts on sexually transmitted diseases (STD)
View CDC's Chlamydia in the United States page
Rates presented are per 100,000 population and are based on the 2000 U.S. Census.
| Cases | Incidence Rate |
|
| Total | 15,294 | 251.5 |
| Race-specific cases and rates1 | ||
| White | 5,530 | 104.0 |
| Black | 6,328 | 1240.7 |
| Other2 | 595 | 237.6 |
| Sex-specific cases and rates3 | ||
| Female | 11,699 | 377.6 |
| Male | 3,560 | 119.4 |
In 2001, the Indiana State Department of Health (ISDH) received 15,294 reports of patients testing positive for Chlamydia trachomatis, the causative agent of chlamydia. Of all the reportable diseases in Indiana, chlamydia is the most commonly reported. The number of reported cases exceeded that of any previous year and was 9.4% greater than the number of reported cases in 2000.
The incidence rate of chlamydia was 251.5 cases per 100,000 population. The 2001 incidence rate is slightly inflated because the denominator used for these rates was the total number of residents as determined by Census 2000 and does not reflect the increase of the population between 2000 and 2001. However, the trend of increasing incidence during the period 1997-2001 is clear (Figure Chl1). Comparing the total number of cases reported in 2001 to 1997 (9,979), an increase of 53.3% was observed. Inter-year differences ranged from 5.5% (1998-1999) to 17.7% (1999-2000).
This increasing trend reflects endemic chlamydia in the presence of improved ascertainment of cases through time. Increasingly economical and sensitive diagnostic methods were employed through the late 1990's. Additionally, ISDH-funded screening sites have been added in recent years, resulting in more testing among young women. Steadily increasing incidence, therefore, does not necessarily reflect increasing propagation of this pathogen among Hoosiers. Rather, sensitivity of the surveillance system is increasing in response to expanded screening of those at risk.
Women are overrepresented among those diagnosed with chlamydia. Known female infections (11,699) exceeded those among males (3,560) by over three-fold. Chlamydia screening programs preferentially test females, because untreated infections cause reproductive sequelae. Pelvic inflammatory disease, a substantial proportion of which is caused by infection with C. trachomatis, is the primary cause of preventable infertility. Federally funded efforts of the Indiana STD Program and the Indiana Family Health Council resulted in selective screening of at-risk young women. Further, male chlamydia infections are often diagnosed as non-gonococcal urethritis, which is not reportable. Because these men do not receive pathogen-specific testing, chlamydia morbidity among males is understated. Therefore, the difference between genders reflects a difference in screening practices rather than greater prevalence among females.
Blacks are overrepresented with respect to this racial group�s contribution to Indiana's total population. While just 8.4% of Indiana�s population was classified as black in the year 2000, over 41% of 2001�s chlamydia cases were reported among this racial group. The race-specific rate for blacks (1240.7) greatly exceeded the race-specific rate for whites (104.0). This racial disparity may be attributable to higher infection rates among people of color, a greater proportion of this subpopulation having received tests in comparison to their white counterparts, underreporting by providers serving non-black patients, or other factors.
Consistent with previous years� distribution by age, the preponderance of cases was among adolescents and young adults (Figure Chl2). In 2001, over 88% of reported cases were among those ages 10-29. The age-group-specific rate for those ages 10-19 was 655.8 per 100,000, while the rate among those ages 20-29 was 910.4 per 100,000.
The three counties with the greatest number of reported cases were Marion (6,542), Lake (1,085), and St. Joseph (931). Marion County cases far exceeded the number reported from any other jurisdiction within Indiana (Figure Chl3 and Table Chl1). While just 14.2% of Indiana's population resides in Marion County, 42.8% of Indiana's reported chlamydia cases were found among Marion County residents. Adjusting for population size, Marion County had the highest incidence rate (760.3), followed by Delaware County (370.5), and St. Joseph County (350.6). Figure Chl3 shows the rates for Indiana counties.
Back to Top of Article
Back to Table of Contents
|
Figure Chl1: Chlamydia - Reported Cases by Year, Indiana, 1997-2001 |
|
|
Back to Reference in Text
Back to Top of Article
|
Figure Chl2: Chlamydia - Incidence Rates by Age Group, Indiana, 2001 |
|
|
Back to Reference in Text
Back to Top of Article
|
Figure Chl3: Chlamydia - Incidence Rates by County, Indiana, 2001 |
|
|
Back to Reference in Text
Back to Top of Article
|
Table Chl1: Chlamydia - Reported Cases by County, Indiana, 2001 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Back to Reference in Text
Back to Top of Article
1 - Race was unknown for 2,841 of the reported cases.
2 - "Other" includes American Indian/Alaska Native, Asian, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, and multiracial.
3 - Sex was unknown for 35 of the reported cases.
* - Rate based on less than 20 cases and should be considered
unstable.
Back to Table of Contents