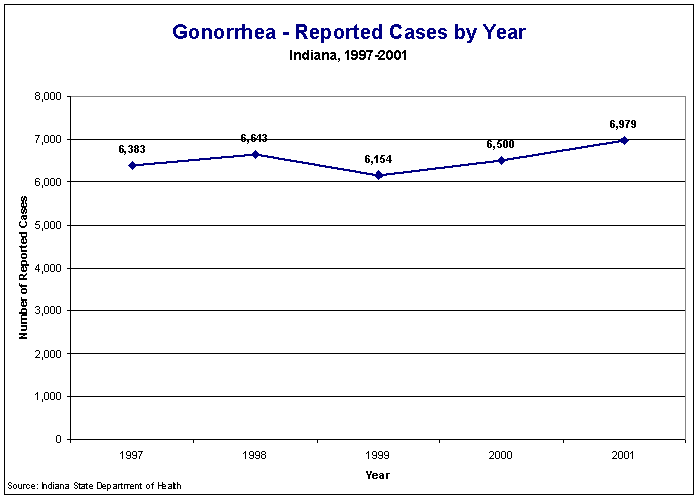
Figure Gon1: Gonorrhea - Reported Cases by Year, Indiana, 1997-2001
2001 Indiana Report of Infectious Diseases |
View ISDH's basic facts on sexually transmitted diseases (STD's)
View CDC's Gonorrhea page
Rates presented are per 100,000 population and are based on the U.S. 2000 Census.
| Cases | Incidence Rate |
|
| Total | 6,979 | 114.8 |
| Race-specific cases and rates1 | ||
| White | 1,457 | 27.4 |
| Black | 4,371 | 857.0 |
| Other2 | 198 | 79.1 |
| Sex-specific cases and rates3 | ||
| Female | 3,795 | 122.5 |
| Male | 3,173 | 106.4 |
In 2001, ISDH received 6,979 reports of patients who tested positive for Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the causative agent of gonorrhea. This sum translates to a crude rate of 114.8 per 100,000 Indiana residents.
Gonorrhea morbidity has been stable during the period 1997 through 2001 (Figure Gon1). The number of case reports ranged from 6,154 known cases in 1999 to 6,979 cases in 2001; 9.3% more cases were reported in 2001 than in 1997 (6,383). Inter-year differences ranged from a decrease of 7.4% from 1998 (6,643) to 1999 (6,154) to an increase of 7.4% from 2000 (6,500) to 2001 (6,979).
The number of cases among women exceeded that of men in 2001. Of cases with known gender, 3,795 female cases were reported, and 3,173 male cases were reported. This gender disparity is consistent with that found in the previous year, but more pronounced. In 2001, the sex specific rate was 122.5 per 100,000 females and 106.4 per 100,000 males, an increase from 113.3 (females) and 105.0 (males) reported in 2000. In terms of gonococcal infections, women were overrepresented with respect to their percentage of Indiana’s population. While comprising just 49.0% of the population, women accounted for 54.5% of the reported gonorrhea infections. Compared with men, greater morbidity among women may be attributable to higher infection rates among females, a greater number of tests among women, or other factors.
In 2001, more cases were reported among blacks than among all other racial groups combined. Of gonorrhea cases with known race, 4,371 (73.5%) were classified as black while 1,457 (24.2%) cases were classified as white. The race-specific rates for blacks (857.0) was higher than that for whites (27.4). Of the total number of cases reported in 2001, 13.7% (953) were of unknown race. Even if all of these cases were among whites, the racial disparity would still be observed. This disparity may be attributable to higher infection rates among blacks, underreporting of gonorrhea among whites, or other factors.
The preponderance of gonorrhea cases was among adolescents and young adults. In 2001, 2,036 cases were reported among those ages 10-19, and 3,382 cases were reported among those ages 20-29; together, these two groups comprised 77.6% of total cases reported. Those ages 10-39 accounted for 91.7% of all reports. The age-specific incidence rate was highest for those ages 20-29 (405.1) and next highest for those ages 10-19 (227.0) (Figure Gon2).
Marion County had a disproportionately high number of cases in 2001. Comprising just 14.2% of Indiana’s population, Marion County contributed 48.4% (3,375 cases) to the 2001 total case count. This translates to an incidence rate of 392.2 cases per 100,000 Marion County residents. Incidence rates for St. Joseph and Allen Counties were 256.8 and 198.0 per 100,000 residents, respectively, also well above the state rate of 114.8 (Table Gon1, Figure Gon3).
Back to Top of Article
Back to Table of Contents
|
Figure Gon1: Gonorrhea - Reported Cases by Year, Indiana, 1997-2001 |
|
|
Back to Reference in Text
Back to Top of Article
|
Figure Gon2: Gonorrhea - Incidence Rates by Age Group, Indiana, 2001 |
|
|
Back to Reference in Text
Back to Top of Article
|
Figure Gon3: Gonorrhea - Incidence Rates by County, Indiana, 2001 |
|
|
Back to Reference in Text
Back to Top of Article
|
Table Gon1: Gonorrhea - Reported Cases by County, Indiana, 2001 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Back to Reference in Text
Back to Top of Article
1 - Race was unknown for 953 of the reported cases.
2 - "Other" includes American Indian/Alaska Native, Asian, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander, and multiracial.
3 - Sex was unknown for 11 of the reported cases.
* - Rate based on less than 20 cases and should be considered unstable.
Back to Table of Contents
[an error occurred while processing this directive]