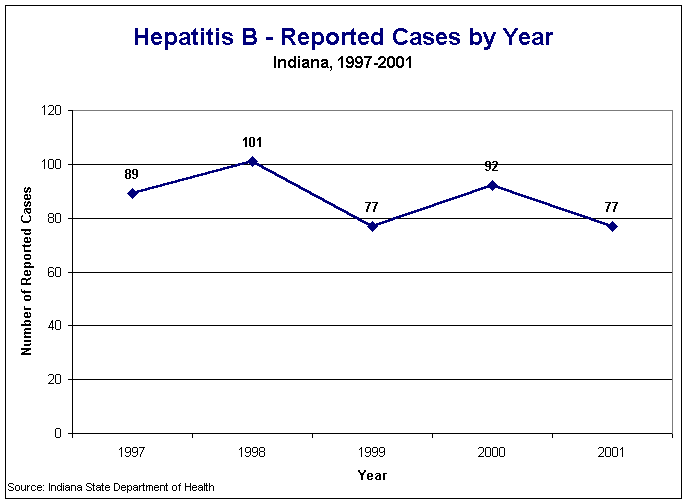
Figure HpB1: Hepatitis B - Reported Cases by Year, Indiana, 1997-2001
2001 Indiana Report of Infectious Diseases |
View ISDH's Quick Facts about Hepatitis B, Hepatitis B Carriers, and Hepatitis B Contacts
View CDC's Hepatitis B page
Rates presented are per 100,000 population and are based on the 2000 U.S. Census.
| Cases | Incidence Rate |
|
| Total | 77 | 1.3 |
| Race-specific cases and rates1 | ||
| White | 44 | 0.8 |
| Black | 18 | 3.5* |
| Other | 0 | |
| Sex-specific cases and rates | ||
| Female | 45 | 1.5 |
| Male | 32 | 1.0 |
Hepatitis B is a bloodborne pathogen disease transmitted by direct contact with blood or body fluids that contain the virus, sexual contact with an infected person, or from an infected mother to her infant during childbirth. The incidence in the United States in 1991 was 7 cases/100,000 population but declined and has remained constant at between 2.5-2.8 cases/100,000 population for the past 3 years. The incidence of hepatitis B in Indiana continues to fall below the national average.
In 2001, 77 cases of acute hepatitis B were reported to the Indiana State Department of Health, matching the previous record low of 1999. One of the reported cases resulted in death. Figure HpB1 shows reported cases of hepatitis B for the five-year period, 1997-2001.
In 2001, rates of acute hepatitis B infection varied with age. The highest age-specific rate in Indiana was found in adults ages 30-39 (2.7) followed by adults ages 20-29 (2.4). Historically, acute hepatitis B rates have been highest in young adults. Figure HpB2 shows the incidence rate of acute hepatitis B by age group.
Although 61 cases were interviewed about risk factors for contracting hepatitis B, not all of those interviewed responded to each question asked (Table HpB1). Having more than one sexual partner continues to be a major risk for acquiring the disease.
In 2001, 26 Indiana counties reported cases of hepatitis B. Incidence rates for counties reporting five (5) or more cases are noted in Table HpB2.
Indiana law requires reporting of both acute and chronic hepatitis B infection during pregnancy and perinatally exposed infants. In 2001, 98 Indiana women were reported as infectious with hepatitis B during pregnancy, compared to 67 in 2000. Identifying these women during pregnancy facilitates appropriate medical treatment for infants. No perinatal transmission was reported.
Back to Top of Article
Back to Table of Contents
|
Figure HpB1: Hepatitis B - Reported Cases by Year, Indiana, 1997-2001 |
|
|
Back to Reference in Text
Back to Top of Article
|
Figure HpB2: Hepatitis B - Incidence Rate by Age Group, Indiana, 2001 |
|
|
Back to Reference in Text
Back to Top of Article
Back to Reference in Text
Back to Top of Article
|
Table HpB2: Hepatitis B - Reported Cases by County, Indiana, 2001 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
Back to Reference in Text
Back to Top of Article
1 - Race was unknown for 15 of the reported cases.
* - Rate based on less than 20 cases and should be considered unstable.
Back to Table of Contents
[an error occurred while processing this directive]