 INDOT inspects pavement on an annual basis. Condition and inventory data is stored within a database that maintains an inventory of all NHS pavement throughout the state of Indiana.
INDOT inspects pavement on an annual basis. Condition and inventory data is stored within a database that maintains an inventory of all NHS pavement throughout the state of Indiana.
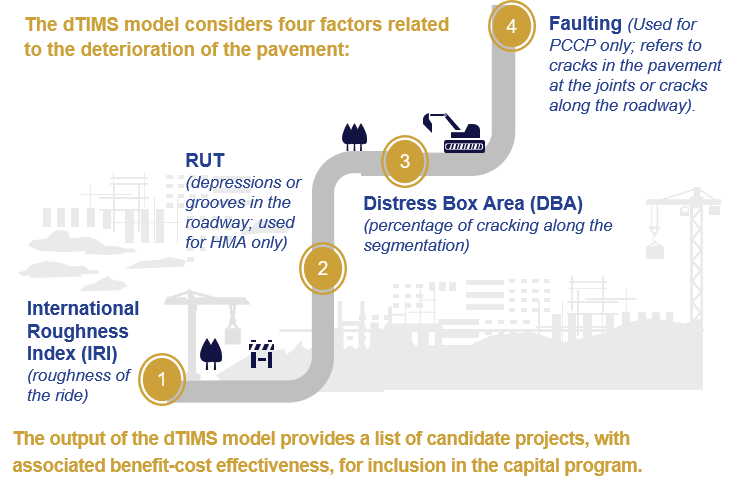
INDOT assesses pavement according to whether pavement is in fair, good, or poor condition, based on the International Roughness Index and Distress Box Area (percentage of cracking), as well as rutting for hot mix asphalt (HMA) pavement and faulting for Portland Cement Concrete Pavement (PCCP).
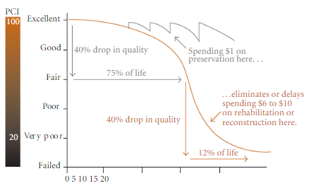
INDOT uses infrastructure management system software for lifecycle cost analyses of pavement. Using data from our pavement database, the software forecasts deterioration for pavement and identifies gaps by comparing it to established condition targets. The software visualizes impacts of various alternative treatment strategies on asset conditions and recommends an optimal, benefit cost-effective strategy for improving the asset condition. The software generates a list of recommended projects that provide the most cost-effective treatment strategies, given anticipated funding constraints and based on the condition and inventory data.
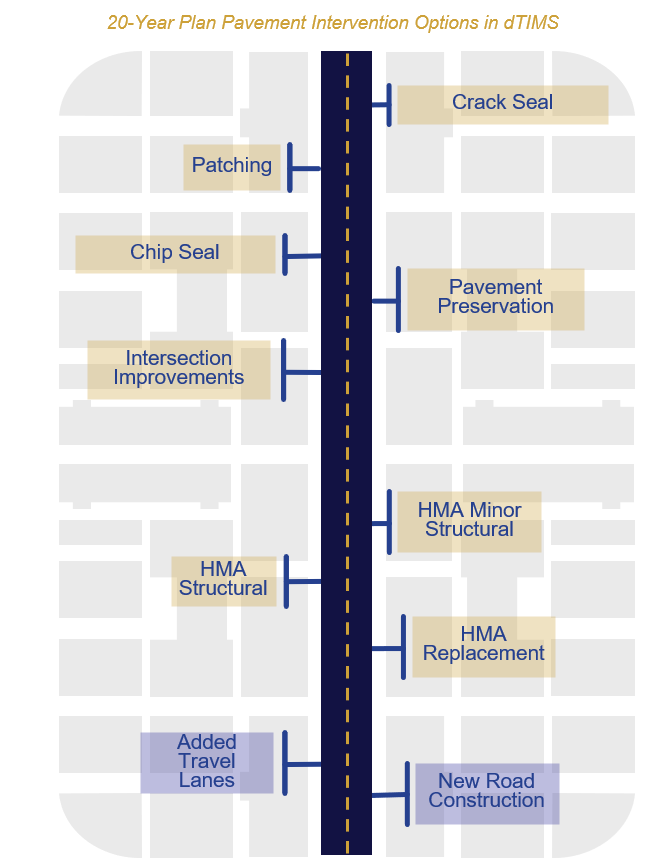
INDOT evaluates the list of projects using a scoring methodology and prioritizes projects to receive funding in the capital program. For HMA pavement, projects are categorized by pavement preservation treatments, preventative maintenance treatments, minor structural treatments, and major structural treatments. For PCCP type pavement, projects are categorized by pavement preservation treatments, preventative maintenance treatments, and major structural treatments.