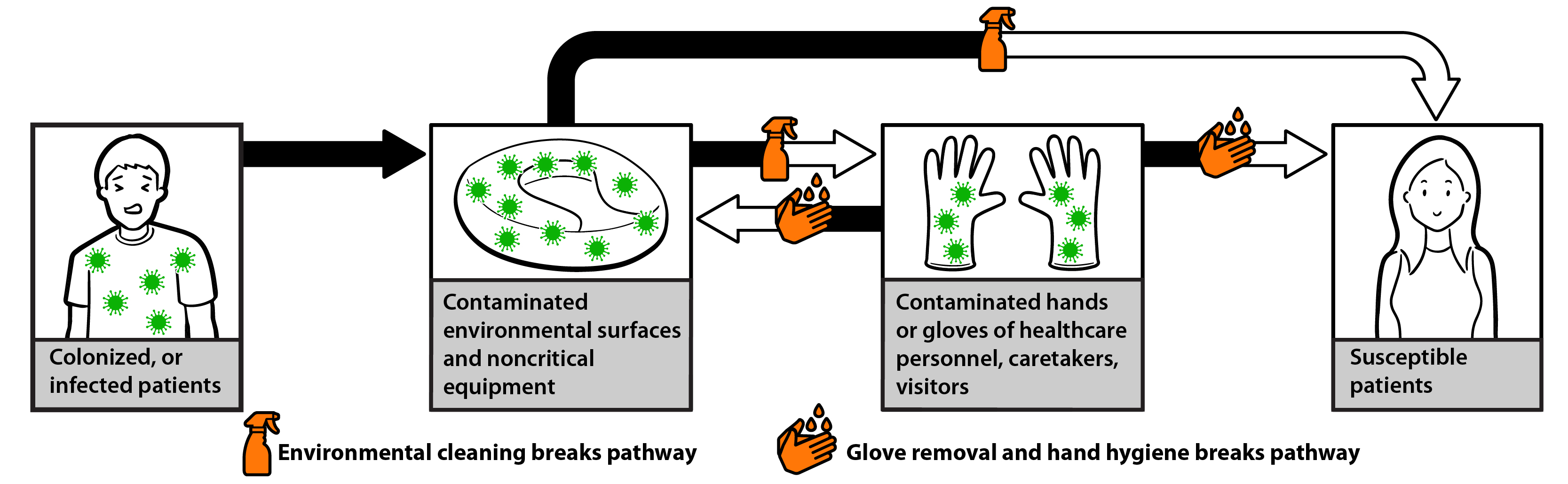
What is Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii complex (MDR-AB)?
Acinetobacter is a genus of gram-negative bacteria that can cause pneumonia, bloodstream infections, and wound infections. Acinetobacter species are found in soil and water, but these bacteria generally do not pose a risk to healthy people. Outbreaks usually occur among severely ill individuals in healthcare settings. Those with weakened immune systems, chronic lung disease, or diabetes are at a greater risk of infection. Around 80% of reported Acinetobacter spp. infections are caused by Acinetobacter baumannii complex. Many strains of Acinetobacter are multidrug-resistant, meaning the strains are resistant to at least one antibiotic in at least three different classes of antibiotics.
Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB)
Carbapenem resistant Acinetobacter baumannii are usually resistant to multiple antibiotics. CRAB can be resistant to carbapenems through different resistant mechanisms. Of biggest concern, are CRAB that produce a carbapenemase. Carbapenemases are enzymes that break down carbapenem antibiotics. Genes that are coded to produce carbapenemases are often found on mobile genetic elements called plasmids. Plasmids can be transferred from one bacteria to another resulting in horizontal gene transmission.