A Continuous Green T (CGT) intersection, also known as a Green T intersection, is a type of 3-leg intersection in which one direction of mainline traffic (opposite to the side street approach) does not have to stop. Vehicles turning left from the mainline to the side road and vehicles turning left from the side road to the mainline are accommodated via physically separated deceleration and acceleration lanes. This eliminates the need for adjacent mainline traffic to stop. A traffic signal controls the opposite direction of mainline traffic, allowing these left turns to occur, just as they do at a traditional intersection. All movements are still accommodated at the intersection, with the added advantage that one direction of traffic on the mainline no longer has to stop at a traffic signal.
Intersections of this type are common and have performed well in other states including Florida, Utah, Nevada, and New York. Green T intersections reduce delay at high-volume locations by removing the need to stop both directions of mainline traffic to accommodate left turns.
INDOT has several Green T intersections in various phases of project development. INDOT’s policy is to use innovative intersections, including the Green T, where appropriate to support its ongoing commitment to improve safety and operational efficiency through innovation and cost-effective investments.
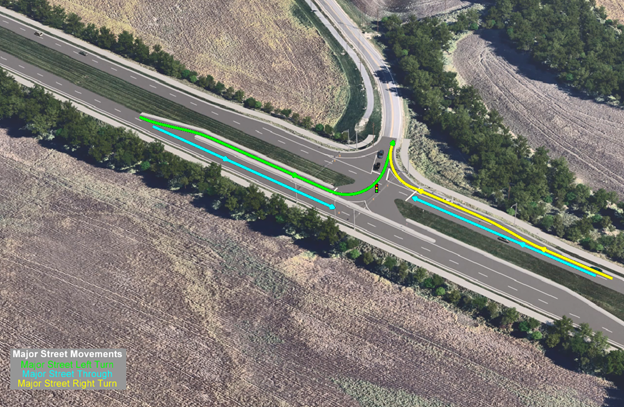

This graphic shows how all the major street vehicle movements work at a Green T intersection.
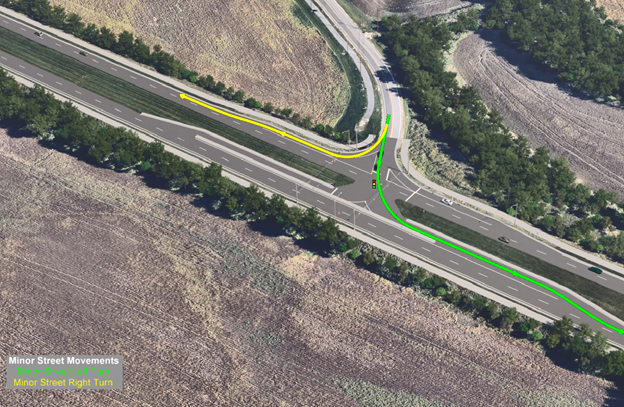
This graphic shows how all the minor street vehicle movements work at a Green T intersection.
